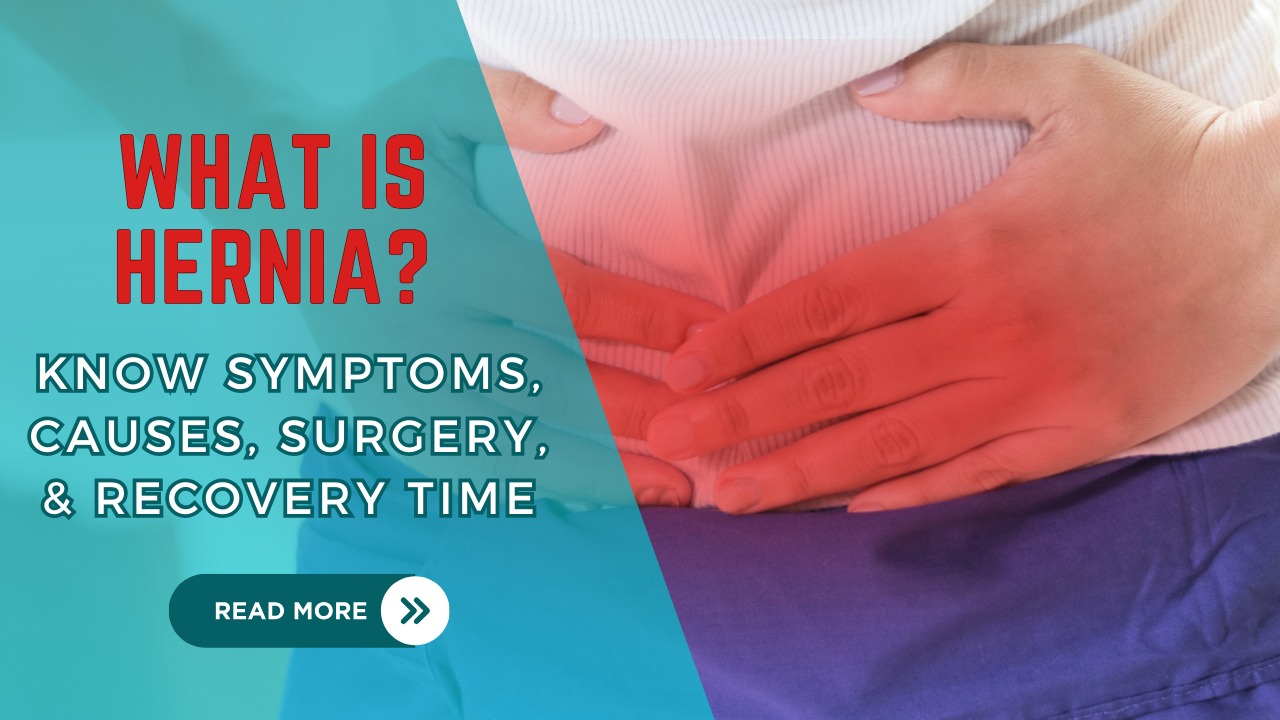
Hernia: Hernias is a common medical condition
that affects millions of people worldwide. While they can occur in various parts
of the body, they most commonly appear in the abdominal region. Understanding
what a hernia is, its symptoms, causes, surgical treatments, and recovery
process is crucial for managing this condition effectively. This comprehensive
guide will provide you with all the information you need to know about hernias.
Understanding Hernias
What is a Hernia?
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue
pushes through a weak spot in the muscle or connective tissue that normally
contains it. This protrusion can cause a noticeable bulge and may lead to
discomfort or pain. Hernias can develop in various parts of the body, but the
most common types are:
●
Inguinal Hernia: Occurs in the groin area.
●
Femoral Hernia: Appears in the upper thigh,
just below the groin.
●
Umbilical Hernia: Found around the belly
button.
●
Hiatal Hernia: Occurs when part of the stomach
pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
●
Incisional Hernia: Develops at the site of a
previous surgical incision.
Symptoms of a Hernia
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of a hernia can vary
depending on its type and location, but common signs include:
●
Visible Bulge: A noticeable lump or bulge
under the skin, especially when standing or straining.
●
Pain or Discomfort: Discomfort or pain at the
site of the bulge, which may worsen with activities like lifting, coughing, or
bending over.
●
Heaviness or Pressure: A feeling of heaviness
or pressure in the abdomen or groin.
●
Burning or Aching Sensation: A burning or
aching sensation at the hernia site.
●
Weakness or Fatigue: General weakness or
fatigue in the affected area.
Symptoms of Specific
Hernia Types
Different types of hernias can have
specific symptoms:
●
Inguinal Hernia: Pain in the groin,
particularly when bending over, coughing, or lifting.
●
Femoral Hernia: Pain and bulging in the upper
thigh.
●
Umbilical Hernia: A bulge near the belly
button, often noticeable in infants and young children.
●
Hiatal Hernia: Heartburn, acid reflux, and
difficulty swallowing.
●
Incisional Hernia: Bulging and discomfort at
the site of a previous surgical incision.
Causes of Hernias
Primary Causes
Hernias can result from a combination of
muscle weakness and strain. Factors that contribute to the development of
hernias include:
●
Genetic Predisposition: A family history of
hernias can increase the risk.
●
Chronic Coughing: Persistent coughing due to
conditions like chronic bronchitis can strain abdominal muscles.
●
Heavy Lifting: Regularly lifting heavy objects
without proper technique can weaken muscles.
●
Obesity: Excess body weight increases the
strain on abdominal muscles.
●
Pregnancy: The additional weight and pressure
during pregnancy can lead to hernias.
●
Constipation: Straining during bowel movements
can contribute to the development of hernias.
● Previous Surgery: Surgical incisions can create weak spots where hernias may develop.
Contributing Factors
Other factors that can contribute to the
development of hernias include:
●
Age: Muscle strength tends to decrease with
age, making older adults more susceptible.
●
Smoking: Smoking can weaken connective
tissues, increasing the risk of hernias.
●
Premature Birth: Babies born prematurely may
have underdeveloped abdominal muscles, increasing the risk of umbilical
hernias.
Diagnosis of Hernias
Physical Examination
Diagnosing a hernia typically involves a
physical examination by a healthcare provider. During the exam, the doctor
will:
●
Check for visible bulges or lumps
in the abdomen or groin.
●
Ask the patient to cough, strain,
or stand to make the hernia more apparent.
●
Assess the size and location of
the hernia.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, additional imaging tests
may be required to confirm the diagnosis and assess the hernia's extent. These
tests may include:
●
Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images
of internal structures.
●
CT Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional
images of the body.
●
MRI: Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to
produce detailed images.
Treatment Options for Hernias
Non-Surgical Treatments
In some cases, especially when the hernia
is small and not causing significant symptoms, non-surgical treatments may be
recommended:
●
Watchful Waiting: Monitoring the hernia for
changes or worsening symptoms.
●
Lifestyle Modifications: Losing weight,
avoiding heavy lifting, and managing chronic cough can help manage symptoms.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is often necessary to repair
hernias and prevent complications. The two main types of hernia surgery are:
Open Surgery
Open surgery involves making an incision
near the hernia site to push the protruding tissue back into place and
reinforce the weakened area with sutures or synthetic mesh. Types of open
surgery include:
●
Herniorrhaphy: Repairs the hernia without
mesh.
●
Hernioplasty: Uses mesh to reinforce the
weakened area.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally
invasive procedure that involves making small incisions and using a laparoscope
(a thin, flexible tube with a camera) to guide the repair. This approach often
results in less pain and a quicker recovery. Types of laparoscopic surgery
include:
●
Transabdominal Preperitoneal (TAPP) Repair:
Accesses the hernia from inside the abdominal cavity.
● Extraperitoneal (TEP) Repair: Accesses
the hernia without entering the abdominal cavity.
Recovery After Hernia Surgery
Immediate Postoperative
Care
Recovery from hernia surgery varies
depending on the type of surgery and the individual's overall health. Key
aspects of immediate postoperative care include:
●
Pain Management: Medications to manage pain
and discomfort.
●
Wound Care: Keeping the surgical site clean
and dry.
●
Activity Restrictions: Avoid strenuous
activities and heavy lifting for a specified period.
Long-Term Recovery
Long-term recovery involves gradually
resuming normal activities while allowing the surgical site to heal. Tips for a
smooth recovery include:
●
Follow- up Appointments: Regular check-ups with
the surgeon to monitor healing.
●
Dietary Adjustments: Eating a balanced diet to
support healing and prevent constipation.
●
Gradual Return to Activity: Slowly increasing
physical activity as recommended by the healthcare provider.
Potential Complications
While hernia surgery is generally safe,
potential complications can include:
●
Infection: Redness, swelling, or drainage at
the surgical site.
●
Recurrence: The hernia may return, requiring
additional surgery.
●
Chronic Pain: Persistent pain at the surgery
site, which may require further treatment.
Preventing Hernias
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can
reduce the risk of developing hernias:
●
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing excess
weight to minimize strain on abdominal muscles.
●
Exercise Regularly: Strengthening core muscles
to support abdominal structures.
●
Practice Proper Lifting Techniques: Using
correct body mechanics to avoid strain.
Managing Chronic
Conditions
Effectively managing chronic conditions
that increase the risk of hernias is also important:
●
Treat Chronic Cough: Addressing underlying
respiratory conditions.
●
Prevent Constipation: Eating a high-fibre diet
and staying hydrated to avoid straining during bowel movements.
When
to Worry About Hernia Pain?
Persistent or Worsening
Pain
●
Seek medical attention if hernia
pain is persistent or worsening, as it may indicate an enlarging hernia or
complications.
Sudden, Severe Pain
●
Sudden, intense pain can signal
serious complications like incarceration or strangulation, requiring immediate
medical intervention.
Accompanying Symptoms
●
Nausea and Vomiting: Possible sign of bowel
obstruction.
●
Fever: May indicate infection or inflammation.
●
Redness and Swelling: Suggests infection.
●
Inability to Pass Gas or Have a Bowel Movement: Indicates bowel obstruction.
Consult with an expert at the Best Hospital in Gwalior ‘Link
Hospital’. If you experience any of these symptoms prevent serious
complications.
Conclusion
Hernias are a common yet manageable
condition that can significantly impact quality of life. Understanding the
symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for early detection and
effective management. With the right medical care and lifestyle adjustments,
individuals with hernias can achieve successful outcomes and a smooth recovery.
If you suspect you have a hernia or are experiencing related symptoms, consult
a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment
plan.
If you experience persistent, severe
hernia pain or any accompanying symptoms, don't delay seeking medical
attention. For expert diagnosis and treatment, trust Link Hospital—The best multispecialist hospital in Gwalior. Our skilled team provides comprehensive care to ensure your health
and well-being. Visit Link Hospital for reliable, top-quality hernia treatment.
Your health is our priority.